37 Animal Cell Under Electron Microscope
We all do not forget that the human physique is quite problematic and a method I. The cell membrane also known as plasma membrane or plasmalemma consists of three layers when viewed under the electron microscope.
Microscopically animal cells from the same tissue of an animal will have varied sizes and shapes due to the lack of a rigid cell wall.
Animal cell under electron microscope. Animal Cell as shown above. IB Biology HLSLA Worksheet Microscopes and Electron micrographs Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells. It has small vacuoles.
6 rows Structure of plant and animal cells under an electron microscope. Some of the cell organelles that can be observed under the light microscope include the cell wall cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus vacuole and chloroplasts. It is an electron micrograph of cells largest and most important organelle the mitochondria and is characterized by the following features Fig.
The Cell as Seen under the Electron Microscope. Diagram Of Animal Cell Under Electron Microscope Labeled. Table D leads to images of electron microscopes or protocols for tissue preparation.
1 The name mitochondria was given by Benda 1898 and their ma n function was brought to light by Kingsbury 1912. Monday April 5th 2021. This atlas offers informative texts on a lot of cell organelles and ultrastructures with detailed information in a generally intelligible way.
It is completed by a vocabulary of microscopic anatomy. In the given figure of an animal cell as observed under an electron microscope. So lets begin by drawing a rough-oval shape.
2 Each mitochondria in section appears as sausage or cup or bowl shaped structure lined by double. Also know what does a animal cell look like under a microscope. But at the same time it is interpretive.
The three layers are composed of one layer of phospholipid sandwiched between two protein layers. The cell membrane is. Animal cells have a basic structure.
View under scanning electron microscope yeast cells of the. Under the intense radiation of the electron microscope 011 electron per Å 2 the question of viability of cells naturally arises because the amount of radiation absorbed during highmagnification imaging is sufficient to cause cell death. Typical Animal Cell With Labels Removed 3.
The ultrastructure of budding and dimorphic yeast cells observed with a scanning electron microscope sem and a transmission electron microscope tem after thin sectioning and freeze etching are then described followed by discussion of the regeneration of the cell wall ofcandida albicans. Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell on the left viewed with the light microscope and on the right with the transmission electron. Beneath a plant cells cell wall is a cell membrane.
Use your ebook to answer the questions below. Plant cell as shown above. Diagram Of Animal Cell Under Electron Microscope.
Most cells both animal and plant range in size between 1 and 100 micrometers and are thus visible only with the aid of a microscope. How is it different from animal cell. Asked Nov 28 2017 in Class IX Science by ashu Premium 930 points.
Typical Animal Cell Pinocytotic vesicle Lysosome Golgi vesicles Golgi vesicles rough ER endoplasmic reticulum Smooth ER no ribosomes Cell plasma membrane Mitochondrion Golgi apparatus Nucleolus Nucleus Centrioles 2 Each composed of 9 microtubule triplets Microtubules Cytoplasm Ribosome 2. Its a thin slice. These cell organelles perform specific functions within the cell.
Heres a diagram of a plant cell. The diagram is very clear and labeled. Summarize two advantages and disadvantages of light microscopes.
Structure of plant and animal. Human cheek cells are made of simple squamous epithelial cells which are flat cells with a round visible nucleus that cover the inside lining of the cheekC. Please show the substitute teacher your completed work as soon as you finish.
Illustrate only a plant cell as seen under electron microscope. However no obvious structural damage was apparent and several repeated scans gave the same images. Under a microscope plant cells from the same source will have a uniform size and shape.
It is flexible and has pores. Cell Structure and Function Student Hadi Yaafar Date May 24 2021 Instructions Please work independently. This feature was lost in the distant past by the single-celled organisms that gave rise to the kingdom Animalia.
Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi animal cells do not have a cell wall. I Name the parts labelled as 1 to 10.
90 Organelles In Both Plant And Animal Cells
Organelles found in both plant and animal cells. Nucleus Plasma Membrane Cell Membrane Endomembranes Endoplasmic Reticulum ER Golgi Complex Vacuole Lysosome Mitochondria Ribosome Peroxisome.
Plant Cell Vs Animal Cell Definition 25 Differences With Cell Organelles
Organelles shared by both plant animal cells.

Organelles in both plant and animal cells. They are jelly-like substances found between the cell membrane and nucleus. Vacuoles are storage sacs for solid or liquid contents. 7 rows Animal cells and plant cells also contain tiny objects called mitochondria in their cytoplasm.
Are they Plant animal or both plant and animal cells. Cell membrane Chromosomes Cytoplasm Mitochondria The plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and contain well developed cellular organelles. The central vacuole of some plant cells may occupy 50-90 of the cell volume.
Their primary function is to -. Golgi apparatus and ribosomes exist in both plant and animal cells. Cell organelle that releases energy in a process called cellular respiration.
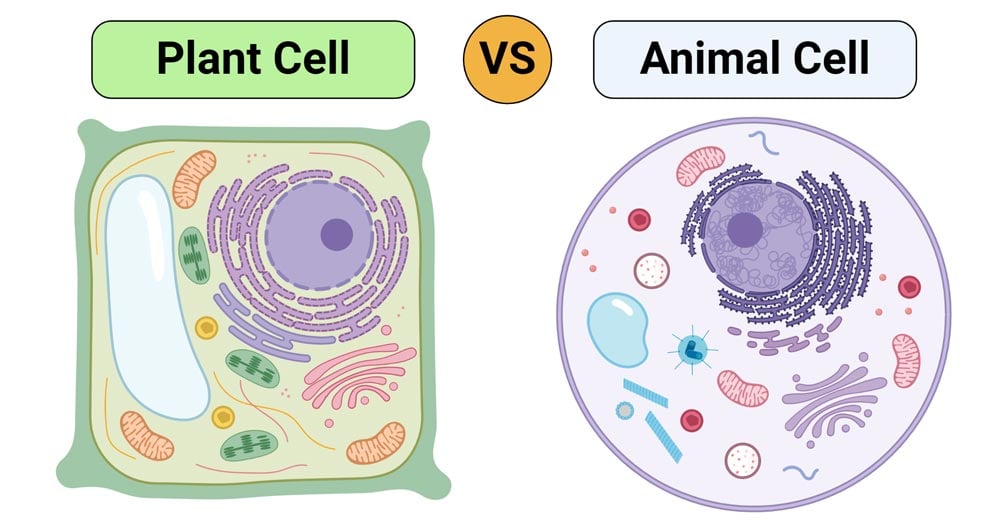
While both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share many similarities they also differ in several ways. Vacuoles are round organelles found in both plant and animal cells. Discuss these differences in relation to the activities of plants and animals.
Amoeba acquires its food by the process of 30. Through how many membranes would a molecule have to pass in going from the interior of a chloroplast to the interior of a mitochondrion. The function of the mitochondria is to break down sugar molecules into ATP energy for both plant and animal cells.
The cytoplasm is one of the essential components of the cell where all the cell organelles are embedded. Vacuoles in animal cells are much smaller. Learn about the key differences between these two cell types in this lesson.
The cell wall and chloroplast are. As stated above both plant and animal cells share a few common cell organelles as. Learn with flashcards games and more for free.
In plant cells vacuoles are full of cell sap and provide turgidity swollen and distended or congested and rigidity to the cell. Rough Smooth Endoplasmic Recticulum. The mitochondria is located in the cytoplasm but outside of the nucleus.
Centrioles exist only in animals but not in plant cells. Secondly what are the main differences between plant and animal cells. Infoldings of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion.
Learn the following terms and their definitions. Structurally plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells. Common organelles of plant animal cells are as follow.
They are mainly composed of water organic and inorganic compounds. The cytoplasm is present both in plant and animal cells. In animal but not plant cells.
They both contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus lysosomes and peroxisomes. Large vacuoles are common in plant cells. The cell membrane cytoplasm chromosomes and mitochondria are the structures that are present in both the plant and.
51 Animal Cell Organelles Diagram
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Animal cell organelles labeled diagram.

The Nucleus And Cytoplasm Anatomy And Physiology
Cell organelle is a specialized entity present inside a particular type of cell that performs a specific function.

Animal cell organelles diagram. Start studying Animal Cell Organelles Diagram. Eukaryotic cells are larger more complex and have evolved more recently than prokaryotes. Cell Organelles definition.
Selectively permeable structure that controls what substances come into and out of a cell. It is mainly made up of water and protein material. The structure of an animal cell differs slightly from a plant cell in terms of shape protective covering and organelles.
Listed below are the Cell Organelles of an animal cell along with their functions. 9 sets of 3 microtubules that are important in cell. There are two types of cells - Prokaryotic and Eucaryotic.
A labeled diagram of the animal cell and its organelles there are two types of cells prokaryotic and eucaryotic. In the labeled animal cell diagram it is nearly circular in shape and lacks outer cell wall. Identify the organelles that are numbered and the function of each organelle by.
Where prokaryotes are just bacteria and archaea eukaryotes are literally everything else. The various cell organelles present in an animal cell are clearly marked in the animal cell diagram provided below. Major cell organelles are as follows.
Start studying Animal Cell Organelles. Animal cell diagram detailing the various organelles Though this animal cell diagram is not representative of any one particular type of cell it provides insight into the primary organelles and the intricate internal structure of most animal cells. Rod-shaped structure that converts energy in food to energy the cell can use.
Its the fluid that contains the organelles. There are various cell organelles out if which some are common in most types of cells like cell membranes nucleus and cytoplasm. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
The cell organelles found in the animal cell are plasma membrane centriole peroxisome lysosome ribosomes mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum cytoplasm nucleus nucleolus nuclear envelope and golgi apparatus. There are various organelles present within the cell and are classified into three categories based on the presence or absence of membrane. 11 Cytosol Its not an organelle.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Start studying Animal cells organelles. The cell membrane is the outer most part of the cell which encloses all the other cell organelles.
8 Smooth endoplasmic reticulum SER. While the plant cell resembles rectangular shape and possesses a rigid cell wall. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts the cell wall and the structure of chromosomal DNA.
An animal cell structure is very complex from other organisms except for plants because there are many organelles present inside the cell of an animal cell. Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus while prokaryotic cells do not. Well-Labelled Diagram of Animal Cell The Cell Organelles are membrane-bound present within the cells.
In short the outer layer of an animal cell is the flexible membrane. Animal cell structure animal cells have a variety of different organelles that work together to allow the cell to perform its functions. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Centrioles are about 500nm long and 200nm in width that are. 5 Rough endoplasmic reticulum RER. A Labeled Diagram of the Animal Cell and its Organelles.
In the labeled animal cell diagram it is nearly circular in shape and lacks outer cell wall. The cell membrane controls the influx of the nutrients and minerals in and out of the cell.
36 Animal Vacuole Cell
In plant cells vacuoles help maintain water balance. They arent needed as much for breaking down substances because lysosomes another organelle in animal cells do that.
Plants Vs Animals Bronco Biology Exploring The Cell
Made of a tough substance called cellulose which supports the cell.

Animal vacuole cell. They are found in both animal and plant cells but are much larger in plant cells. Especially in protozoa single-celled eukaryotic organisms vacuoles are essential cytoplasmic organs organelles performing functions such as storage ingestion digestion excretion and. The vacuoles of the animal cells are useful for overcoming the foreign particles that may be the bacteria.
Plant and animal cell diagrams quiz. Vacuolesare storage bubbles found in cells. Initially the vacuole is like a small bubble.
Vacuoles in animal cells. It is the obligation of the membrane of the cell to invaginate for the prime goal of engulfing the bacteria. Plant cells also have a cell wall and often have chloroplasts and a permanent vacuole.
Vacuole Function in Animal Cells. The vacuole is a type of organelle present in eukaryotic cells. Vacuoles might store food or any variety of nutrients a cell might need to survive.
Sometimes a single vacuole can take up most of the interior space of the plant cell. Plant cells consist of a cell wall which helps to protect and support the cell. This enhanced visual instructional tool assists in grasping and retaining the names of the cell parts like mitochondrion vacuole.
In this process a vacuole is formed. Some animal cells do not have vacuoles. Vacuole in biology a space within a cell that is empty of cytoplasm lined with a membrane and filled with fluid.
However some protists animal cells and bacteria also contain vacuoles. In animal cells vacuoles are generally small and help sequester waste products. Contains a liquid called cell sap which keeps the cell firm.
It contain fluid called cell SAP which consists of water sugar amino acids in Science salt nitrogenous waste etc. It becomes larger as the cell grows. In animal cells they are small and typically transport materials into and out of the cell.
In animal cells vacuoles tend to play a lesser role. Animal cell vacuoles are much smaller than plant or fungal vacuoles and animal cells generally have multiple vacuoles. Vacuoles can store different substances depending on the type of cell they are in.
In animal cells vacuoles perform a more subordinate role as mediating storage units and carriers during exocytosis and endocytosis. It is a sac surrounded by a single membrane called a tonoplast. Animal cells usually have an irregular shape and plant cells usually have a regular shape.
Vacuoles are fluid-filled enclosed structures that are separated from the cytoplasm by a single membrane. Even though plant cells and animal cells both have vacuoles the vacuole present in the plant cell is much larger compared to the one in the animal cell. For example in fat cells vacuoles will often store large amounts of lipids.
The plant vacuole stores water whereas animal vacuole store nutrients ions waste products and water The plant vacuole is located at the center of the cell while animal vacuole is distributed all over the cell. A vacuole is a membrane-bound cell organelle. The animal vacuole is suitable for exocytosis and endocytosis whereas plant cell is responsible for maintaining turgor pressure.
They can even store waste products so the rest of the cell is protected from contamination. Plant and animal cells. The main function of vacuoles in animal cells is to isolate and remove waste products from.
Animal cell vacuoles are typically small and each cell can contain multiple vacuoles. Vacuoles in animal cells mostly store substances. Vacuoles serve many functions depending on the needs of the cell.
They are found mostly in plant cells and fungi. A vacuole is an organelle inside plant and animal cells that stores water and some wasteAn animal has small vacuoles which are barely more than large vesicl. Vacuoles are storage sacs or cavities in which solid or liquid is stored in the cell.
Although animal cells contain vacuoles they do not contain large central vacuoles. A vacuole is a cell organelle found in a number of different cell types.
23+ Animal Cell Structure And Function
Almost all animals and plants are made up of cells. Allows materials in and out.
This genetic information is called deoxyribonucleic acid dna.
Animal cell structure and function. Structure and Characteristics of an Animal Cell. Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. Animal cells have centrioles which are absent in plant cells.
An animal cell is the smallest unit that makes up the varied tissues of animal species. Animal cells have a. The most common types of animal cells are.
They are considered to be multicellular organisms. A protective layer that forms the cells surface and allows waste nutrients and oxygen to enter and leave the cell. The red blood cells make up the blood while the nerve cells make up the nervous system tissues.
An animal cell is defined as the basic structural and functional unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Animalia. In addition they have locomotory and cytoskeletal structures. Cytoplasm Jelly-like fluid that surrounds and protects the organelles.
Animal cells vary in different shapes and size and perform specific functions. Ribosome small organelles composed of rna rich cytoplasmic granules that are sites of protein synthesis. Animal cell diagram and functions.
A group of cells assemble together to form tissues and eventually to organs and organ systems. PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLPLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS SSS Organelle Function Cell Membrane A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
Lysosome Contains digestive enzymes that destroy damaged organelles and invaders. Animal Cell Definition Structure Parts Functions And Diagram Dna contains all the. They have a distinct nucleus with all cellular organelles enclosed in a membrane and thus called a eukaryotic cell.
Your child can now study science from the comfort of their own home from the wide array of science videos available on the DP Education - Science YouTube cha. Vary in both size and form Cytology-is the study of cell. Animal cells have an organized nucleus with the nuclear envelope.
Intake of nutrients Movement Growth Response to stimuli Exchange of gases Waste removal Reproduction Various organelles of a cell work together to meet the. In Unit 7 an introduction to the form and function of the animal body is followed by chapters on specific body systems and processes. There are hundreds of cell types in a developed organism which are specific to their location and function.
This unit touches on the biology of all organisms while maintaining an engaging focus on human anatomy and physiology that helps students connect to. Melanocytes keratinocytes Merkel cells and Langerhans cells. Cell Structure and Organelles Each eukaryotic cell contains specialized parts called organelles that carry out specific functions necessary for life Each organelle has a specific function such as.
Cytoplasm is supposed to be the matrix or gel like substancefluid present inside the cell.